In a world filled with uncertainties, understanding risk management is essential, whether in daily life or professional settings, such as in companies. This is because every action comes with its own risks, whether positive or negative.
In daily life, for instance, even simple decisions, such as choosing what to eat, are accompanied by risks. Does the chosen food provide proper nutrition for the body, or does it have the opposite effect?
Similarly, in a corporate setting, managing risk is an integral part of handling various challenges. For example, companies often face the risk of currency fluctuations in international transactions. To manage such risks, companies may use hedging contracts like forwards or currency options, maintain reserves in foreign currencies to meet potential needs, or review and adjust budgets based on exchange rate trends.
For this reason, understanding risk management is crucial, especially for companies. The following discussion will explore what risk management entails and how to effectively implement it.
What Is Risk Management?

Risk management is the process of evaluating, analyzing, and controlling risks. The purpose of risk control is to minimize potential losses while maximizing opportunities more efficiently.
In risk management, there are several aspects that companies must understand to ensure that the identification, analysis, and mitigation of risks can influence key areas of focus, such as:
1. Decisions to Be Made
Sound decision-making can reduce negative impacts and maximize benefits. It also influences the sustainability of a company’s strategy, including risk mitigation strategies (avoiding, reducing, accepting, or transferring risks).
2. Time, Location, Specific Factors, and the one Excluded
This aspect refers to:
- Time: The duration of implementation, whether focused on a specific period or ongoing.
- Location: The physical or virtual area where risks may arise.
- Specific Factors: Priority elements for management focus, such as processes, assets, or external relationships.
- Exclusions: Unpredictable factors or uncontrollable risks to prevent confusion, such as risks beyond the organization’s control.
3. Required Resources
Risk management also involves understanding the allocation of resources necessary to ensure effective processes. These resources include:
- Risk Management Team: A group of individuals with expertise in identifying, analyzing, and managing risks. This team coordinates risk management efforts across the organization.
- Budget: Funds allocated to support risk management activities, including training, technology implementation, and strategy development.
- Historical Data: Information from past risk events used to identify patterns and predict potential future risks.
Who is Responsible for risk management? typically falls on the risk owner—an individual or team tasked with managing specific risks and overseeing their impacts. This ensures proper monitoring and handling to mitigate any adverse effects.
Differences Between Reactive and Proactive Risk Management

Risk management can be approached using two primary strategies: reactive and proactive.
1. Reactive Strategy
A reactive strategy focuses on addressing risks or issues after they have occurred. Like a “firefighter,” this approach aims to minimize the negative impact of situations that have already happened. It is typically employed when risks are unavoidable or were undetected beforehand.
For example, consider a technology company suddenly facing a cyberattack that disrupts its systems. With a reactive strategy, the company would immediately activate emergency protocols, repair the affected systems, and recover lost data. Afterward, they would analyze the root cause of the issue to prevent similar incidents in the future. In essence, a reactive strategy is about “fixing the problem after it happens.”
2. Proactive Strategy
A proactive strategy emphasizes prevention and anticipation of risks before problems arise. It is akin to “building a dam before the flood.” This approach involves identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and taking measures to reduce the likelihood of their occurrence or minimize their effects if they do occur.
For instance, in the same technology company scenario, a proactive strategy would mean the company has already implemented advanced security systems, data encryption protocols, and regular employee training to recognize cyber threats. Even before an attack occurs, they have mitigated the risks, ensuring minimal or no impact.
Both approaches are important, but adopting a proactive strategy often leads to greater resilience and preparedness, reducing the need for reactive measures.
Discover more: Effective Problem-Solving Methods in Teams
Benefits of Risk Management for Business Sustainability

Effective risk management enhances a company’s performance, directly influencing organizational sustainability and increasing the success of strategies aimed at creating a safe environment and fostering long-term growth. Additionally, the following key benefits can be achieved:
1. Protecting Financial Stability
Effective risk management enables organizations to anticipate potential market fluctuations, currency exchange changes, and other financial risks. This helps prevent significant losses that could disrupt operational continuity.
2. Ensuring Operational Continuity
Operational risks, such as technology disruptions or supply chain interruptions, can hinder productivity. With proper risk management, organizations can ensure that business processes run smoothly without significant disruptions.
3. Supporting Regulatory Compliance
Risk management also ensures that organizations adhere to applicable laws and regulations. This not only protects companies from penalties or fines but also helps maintain positive relationships with stakeholders.
4. Preserving Reputation
Product or service failures can damage public trust in an organization. By proactively managing reputational risks, companies can maintain a positive image and continue earning customer confidence.
5. Enhancing Competitiveness
Comprehensive risk management provides organizations with an advantage in facing challenges and seizing opportunities. It allows companies to become more adaptive, innovative, and competitive in an ever-changing market.
Through these benefits, risk management becomes a critical element in building resilience and ensuring long-term success for any organization.
Types of Risk Management

Risk management encompasses a variety of approaches. To better understand, here are the different types of risk management:
1. Loss-Based Management
This approach evaluates risks based on potential losses and their likelihood of occurrence, allocating resources to manage risks with the greatest impact.
2. Project-Based Risk Management
This approach is applied within specific project contexts, identifying and controlling risks to achieve project goals while minimizing disruptions.
3. Qualitative Risk Management
This involves subjective, quality-based assessments to identify and measure risks, often relying on expert insights and experience. For example, panel discussions are used to evaluate risks from a managerial perspective.
4. Quantitative Risk Management
This approach relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to assess risks. Mathematical models are employed to measure potential impacts and probabilities. For instance, Monte Carlo simulations are used to estimate the financial impact of risks.
5. Dynamic Risk Management
This focuses on continuous monitoring and adjustment of risks as they evolve over time, especially in rapidly changing environments. For example, updating marketing strategies in real-time based on shifting market trends.
These types of risk management provide organizations with diverse tools to address risks effectively in various scenarios.
5 Steps to Create Effective Risk Management
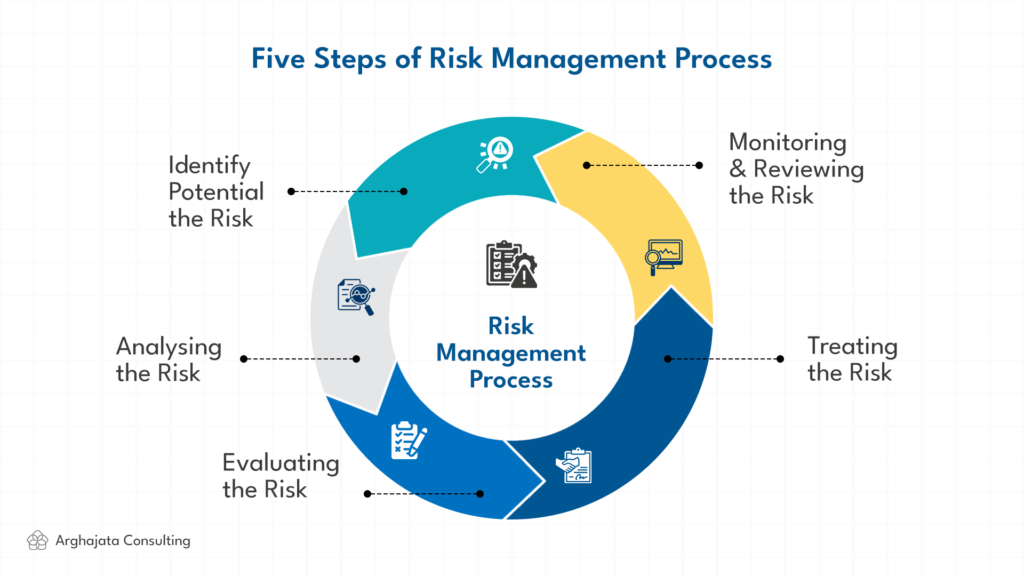
To establish effective risk management, the following steps can be undertaken:
1. Risk Identification
The first step is to identify all potential risks that could impact organizational objectives, whether they are financial, operational, legal, or external in nature. This process can be conducted through brainstorming sessions, interviews, or historical data analysis.
2. Risk Analysis
Once risks are identified, the next step is to analyze their potential impact on the organization. This analysis can be performed in two ways:
- Qualitative Analysis: Assessing the severity of the risk.
- Quantitative Analysis: Calculating potential losses numerically.
3. Risk Evaluation
At this stage, organizations prioritize risk management efforts based on the level of impact and likelihood of occurrence. Risks with significant negative impacts should be avoided, while risks that present opportunities should be strategically leveraged.
4. Risk Control
Following evaluation, risk control measures are implemented. This process involves adopting policies, procedures, or technologies to mitigate the impact of identified risks.
5. Risk Monitoring and Review
Risks are not static. Organizations must regularly monitor, re-evaluate, and adjust risk management strategies in response to changes in the business environment and market conditions.
By following these steps, organizations can build a robust risk management framework that supports sustainable growth and resilience.
Challenges in Risk Management
Even with a comprehensive risk management approach, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. These challenges include:
- Difficulty in predicting complex risks.
- The high level of uncertainty in the global market, which is an inherent aspect of risk control.
- A lack of resources or accurate data to assess risks within the company, potentially leading to discrepancies in risk management plans.
Discover more: Due Diligence as a Foundation for Companies to Assess Potential Risks
To address these challenges, five methods for overcoming risk management challenges can be implemented:
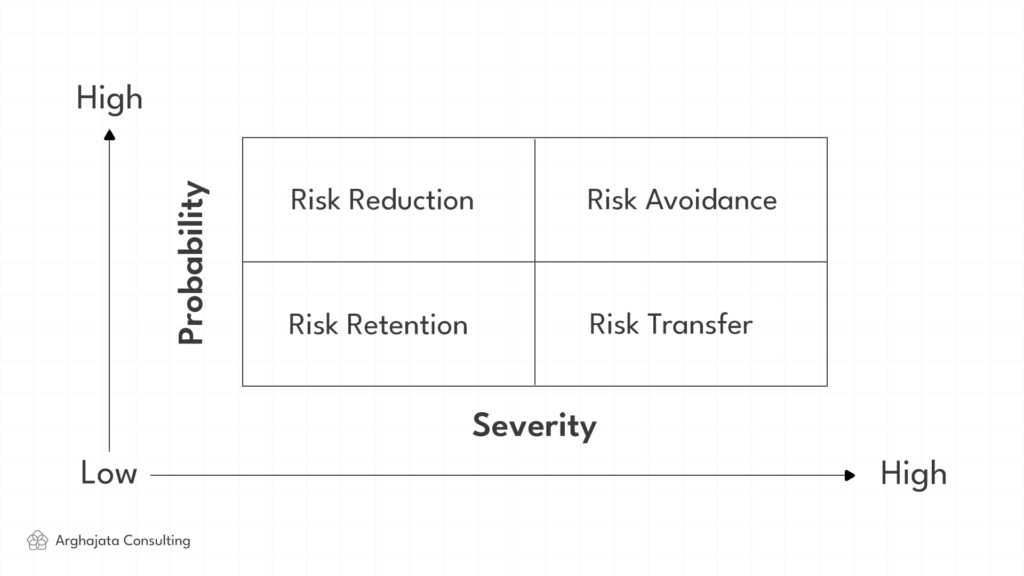
1. Risk Avoidance
This involves taking steps to eliminate potential threats by not engaging in activities that pose significant risks. This method is used when the risk is deemed too threatening and unacceptable for the organization. For example, in a construction project, the company chooses a location safe from natural disasters, such as floods or landslides, to avoid substantial losses.
2. Risk Reduction
This entails minimizing the likelihood of risks occurring and their potential impact through professional measures. For example, a company implements cybersecurity technology to reduce the likelihood of cyberattacks.
3. Risk Transfer
This method involves transferring risks, whether they have occurred or are potential threats, to another party, usually through contracts or insurance. For example, using insurance to anticipate potential losses, such as asset damage or health-related incidents.
4. Risk Retention
Accepting risks without taking action, usually because their impact is considered minor or as a way to gain market insights.
For example, an F&B company accepts the risk of failure for its first product launch as part of the learning process.
These methods are chosen based on the level of risk, its impact, and the organization’s capacity to manage it. Often, organizations combine several methods to address different types of risks.
According to a recent study by Harvard Business Review (2024), many companies face difficulties in fully integrating risk management into strategic decision-making, especially when dealing with unexpected risks such as pandemics or natural disasters.
Through effective risk management, organizations can mitigate negative impacts, optimize decision-making, and maintain long-term stability. At Arghajatha Consulting, we are committed to helping you design structured and effective risk management strategies.
Entrust your risk management needs to us, and together, we will create an organization that is resilient, adaptive, and ready to face any challenge.
[Article Reviewed and Approved by Athiya K. Maghfira/Consultant]

















